The landscape of energy efficiency is ever-changing. New technologies and approaches are emerging that are transforming the way we use and conserve energy. As our understanding of energy efficiency evolves, so too do the ways in which we can make our businesses more energy efficient. From solar panels to LED lighting, from benchmarks to building upgrades there are a variety of options available to help save energy and money.
States are continuing to adopt ordinances and laws, that make it easier for business owners and businesses to “go green.” Some of these laws and ordinances are designed to increase the use of renewable energy, while others aim to improve energy efficiency. These laws and ordinances are always changing and updating, with new laws coming into effect every year.
Many states are mandating compliance with the updated International Energy Conservation Code (IECC), which includes provisions for increased energy efficiency in commercial buildings. The code is updated every three years, with the most recent version being published in 2021. The 2024 IECC will be more stringent than the 2021 IECC in terms of overall energy performance. The ICC board gave the committee this directive: “The code is updated on a three-year cycle with each subsequent edition providing increased energy savings over the prior edition.”
The IECC provides a minimum baseline for Energy Efficiency standards that must be met or exceeded to obtain a building permit. The code is designed to reduce energy consumption and encourage the use of energy-efficient practices and technologies. Some of the provisions of the IECC include:
| Commercial | Non-Commercial |
| Improved insulation for walls, ceilings, floors, and windows | Improved insulation for walls, ceilings, floors, and windows |
| Reduced air leakage through cracks and openings in the building envelope | Reduced air leakage through cracks and openings in the building envelope |
| More efficient heating and cooling systems | More efficient heating and cooling systems |
| Improved lighting efficiency | X |
| Reduced water consumption | X |
| Improved ventilation rates | X |
As you can see the IECC includes additional requirements and provisions for commercial buildings. Many cities and states are also adopting additional energy efficiency measures beyond what is required by the IECC, particularly for existing commercial buildings. These measures can vary from state to state, but some common examples include offering incentives to businesses to make energy efficiency improvements and establishing building energy codes that are more stringent than the IECC.
Additional energy efficiency measures such as energy benchmarks and disclosure for commercial buildings are becoming more and more prevalent across the United States. This means that owners of commercial buildings must track their energy use and report it to the state on a regular basis. With 32 Benchmark Laws adopted in 2021, which increased to 45 by 2022, and at least 6 more coming into effect in 2023, it’s ever apparent that energy benchmarking will continue to play a vital role for more and more cities in the years to come.
As the number of Benchmark Laws increases every year, so do the mandates for Energy audits and other additional requirements. For instance, commercial buildings will soon be required to supply part, if not all, of their own electrical usage through sustainable means. By making energy use more transparent, building owners are encouraged to make improvements that can save money and help the environment. The goal of these measures is to promote energy efficiency and help reduce energy consumption.
The trend toward more energy-efficient businesses is likely to continue in the years ahead, as we look for ways to save energy and money with new technologies and approaches. As the landscape of energy efficiency continues to adapt and change, there are sure to be new and exciting developments in the field that we can all benefit from.
Beginning in 2023, VertPro® will be switching to online payments only, following suit with paper-free companies such as Google, Apple, and Facebook. Join the paper-free revolution with VertPro® and enjoy all the same benefits in a more environmentally friendly way!
Mountain View Seismic Ordinance

Following suit with many other California cities, Mountain View is mandating the retrofit of unreinforced masonry-bearing wall buildings constructed prior to 1933. The provisions of City code Article x111. – Earthquake Hazard Reduction in Existing Buildings depicts minimum standards for structural seismic resistance established primarily to reduce the risk of loss of life or injury and to reduce earthquake damage to rehabilitated buildings. So, what does this mean for Mountain View?
In the United States, seismic ordinances have been adopted in several jurisdictions, including California, Oregon, and Washington. These ordinances generally require the evaluation of buildings identified as being vulnerable to earthquake damage and the implementation of specific retrofit measures if the building is found to be deficient. The type of buildings typically covered by these ordinances includes unreinforced masonry buildings, soft-story buildings, and non-ductile concrete buildings. These requirements address critical safety concerns by increasing the likelihood that occupants can safely exit the building in the event of an earthquake.
Historically, many of these ordinances were passed because of devastating earthquakes. The 1994 Northridge earthquake resulted in 57 deaths and over $20 billion in damage. The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake caused 63 deaths and over $12 billion in damage. And the 1971 San Fernando earthquake resulted in 65 deaths and over $500 million in damage. These earthquakes – and others like them – led to a greater understanding of the importance of seismic safety. As a result, cities began mandating retrofits for buildings of a certain age and construction type. If your building falls into one of these categories, it’s important to get in compliance as soon as possible.
Unfortunately, many buildings in California are at risk of collapse during an earthquake. A study by the US Geological Survey found that, in a major earthquake, up to 28% of wood-frame soft-story buildings could collapse. Wood-frame soft-story buildings make up a large portion of the housing stock in California – an estimated 60% of all apartments in the state are soft-story buildings. Different cities in California have different seismic retrofit ordinances. The City of Los Angeles passed its Seismic Retrofit Ordinance in 2015, which applies to wood-frame soft-story buildings and non-ductile concrete buildings. San Francisco’s Soft-Story Program applies to wood-frame buildings with five or more stories that have soft, weak, or open-front walls and were built before 1978. And Berkeley’s Seismic Retrofit Program applies to all buildings, regardless of construction type or year built.
Mountain View is now mandating all buildings constructed or under construction prior to 1933 which have bearing walls constructed of unreinforced masonry to be retrofitted. Unreinforced masonry buildings are defined as any building built prior to 1933 containing walls constructed wholly or partially with any of the following materials:
- • Unreinforced brick masonry
- • Unreinforced concrete masonry
- • Hollow clay tile
- • Adobe or unburned clay masonry
- • Any other unreinforced tile or masonry construction material.
“This article shall not apply to group M occupancies; detached group R, division 3 occupancies; detached group R, division 1 occupancies with less than five (5) dwelling units used solely for residential purposes; nor to any undamaged building less than nine hundred (900) square feet and containing less than five (5) occupants as determined by 33-A of the 1985 Uniform Building Code.” Source
Time Limits for Compliance starting from August 12, 2022
Structural Analysis
REQUIRED ACTION BY THE OWNER | TIME FRAME FOR COMPLIANCE |
The building owner submits structural analysis or other data indicating that the building complies with this article; or | 270 calendar days from. |
The building owner submits structural analysis and plans for proposed structural alterations of the building to ensure compliance; or | 270 calendar days from. |
The building owner submits plans for the demolition of the building. | 270 calendar days from. |
Structural Upgrade
REQUIRED ACTION BY THE OWNER | TIME FRAME FOR COMPLIANCE |
The City council shall establish a mandatory compliance date for completion of the URM building structural upgrade for demolition. | Within 120 calendar days from the end of the 270-calendar day structural analysis period. |
Letter of Intent
REQUIRED ACTION BY THE OWNER | TIME FRAME FOR COMPLIANCE |
The building owner shall submit a letter of intent to the building official stating intent to upgrade or demolish the building. | Within 180 calendar days after the council adopts the mandatory compliance date. |
1 Where two (2) or more adjacent buildings under separate ownership are to be rehabilitated simultaneously, an extension may be allowed, with a suggested minimum extension of six (6) months. An extension could be granted on submission of a binding agreement between the owners involved, with the actual date of compliance to be determined by the chief building official.
Furthermore, while Mountain View does not currently mandate the retrofit of wood-frame soft-story buildings (as of January 2022) it is likely the city soon will, and this provision will apply to existing buildings that have the following characteristics:
• Ground-floor wood-frame construction with an open layout
• Minimum of two stories
• Three or more dwelling units on a single parcel of land
• Constructed prior to approximately 1980
The May 2018 Mountain View Soft Story Study Report, estimates that approximately 488 buildings within the City of Mountain View would fall within the scope of this potential wood-frame soft-story building ordinance. The 488 buildings identified within the survey have at least three residential units, a total of 5,123 housing units which represents about 16 percent of the city’s total housing, which rivals the percentage of earthquake-vulnerable homes in Oakland and San Francisco.
Seismic retrofitting is vital for the safety of your tenants, employees, and customers. It’s also required by law in many cases and can result in heavy fines from the city for non-compliance. Additionally, if your building is found to be at risk of collapse in an earthquake, you may be ordered to vacate the premises until the retrofit is complete. Check with your city to see what ordinances apply to your commercial building, don’t wait until it’s too late – retrofit your building today and help ensure the safety of everyone inside.
New Energy Benchmark Laws for 2023
 As more and more states look to benchmarking to improve energy efficiency, several new laws and ordinances are set to go into effect in 2023. These laws will require benchmarking for all commercial buildings over a certain size and will impose penalties for those that do not comply.
While some building owners may see this as a burden, benchmarking can be a valuable tool. It can help identify areas where a building is wasting energy and can also help reduce a building’s energy consumption and be more sustainable. In the long run, benchmarking can save building owners money by helping them make their buildings more efficient.
Not only are new laws and ordinances being implemented, but existing laws are constantly being updated. These updates include lowering the size threshold for buildings covered by the benchmarking requirements, establishing new third-party data verification requirements, requiring the use of whole-building utility data, including aggregate data directly from utilities when applicable, and clarification of violations and the enforcement process.
As more and more states look to benchmarking to improve energy efficiency, several new laws and ordinances are set to go into effect in 2023. These laws will require benchmarking for all commercial buildings over a certain size and will impose penalties for those that do not comply.
While some building owners may see this as a burden, benchmarking can be a valuable tool. It can help identify areas where a building is wasting energy and can also help reduce a building’s energy consumption and be more sustainable. In the long run, benchmarking can save building owners money by helping them make their buildings more efficient.
Not only are new laws and ordinances being implemented, but existing laws are constantly being updated. These updates include lowering the size threshold for buildings covered by the benchmarking requirements, establishing new third-party data verification requirements, requiring the use of whole-building utility data, including aggregate data directly from utilities when applicable, and clarification of violations and the enforcement process.
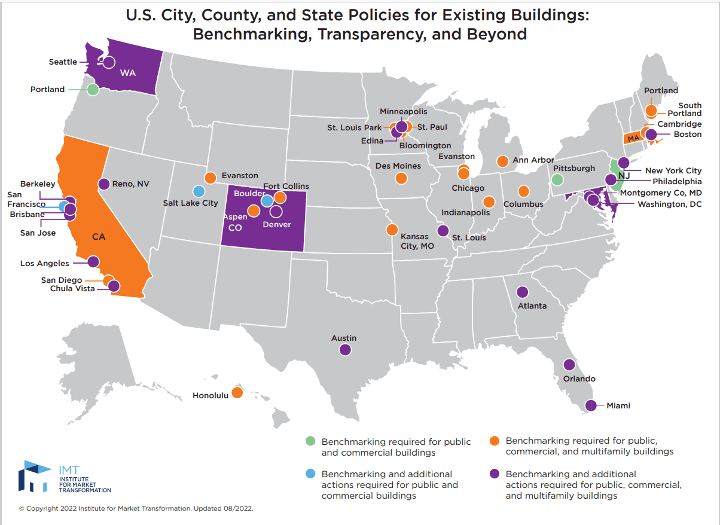 Source: IMT Benchmarking Map 08312022 CURRENT
If you own a commercial building, now is the time to start getting ready for the new benchmarking laws, and if you’re not already benchmarking your building, now is a good time to start. Many new states will require benchmarking compliance in 2023 and will enforce penalties on those who do not follow the new benchmarking laws. However, benchmarking can be simple and easy with the help of Vert Energy Group! Once you know where your building stands in terms of energy efficiency, you can make changes to ensure that your property is as efficient as possible with VertPro®.
Source: IMT Benchmarking Map 08312022 CURRENT
If you own a commercial building, now is the time to start getting ready for the new benchmarking laws, and if you’re not already benchmarking your building, now is a good time to start. Many new states will require benchmarking compliance in 2023 and will enforce penalties on those who do not follow the new benchmarking laws. However, benchmarking can be simple and easy with the help of Vert Energy Group! Once you know where your building stands in terms of energy efficiency, you can make changes to ensure that your property is as efficient as possible with VertPro®.
"I have a firm belief in the ability and power of women to achieve the things they want to achieve" - Eleanor Roosevelt
A Brief History of Labor Day
 In the United States, Labor Day is celebrated on the first Monday of September. It’s a day off for many workers, and a time to enjoy the last few days of summer, but did you know that Labor Day is more than just a day off from work? This American institution has a long and interesting history so let’s take a quick look at the origins of Labor Day and how it’s evolved over the years.
Labor Day has its roots in the labor movement of the late 19th century. At that time, working conditions were often very dangerous, and workers were frequently required to work long hours for little pay. In an effort to improve these conditions, workers began organizing into unions. On September 5, 1882, 10,000 workers took unpaid leave and marched in New York City to demand better working conditions. The following year, another labor parade was held in New York City. Inspired by these events, workers across the country began holding their own parades and rallies on the first Monday in September.
In 1884, the first formal proposal to make Labor Day a national holiday was made at a meeting of the Central Labor Union. The proposal was approved, and the first National Labor Day was celebrated on September 5, 1884. In 1894, Congress passed a law making the first Monday in September, a national holiday, Labor Day. The first Monday in September was selected as the official date for a few reasons: first, it allowed workers a three-day weekend (as Friday and Saturday were already days off); second, it prevented summer vacations from being cut short; and third, it avoided competition with Independence Day celebrations. Today, Labor Day is celebrated in countries around the world to recognize the achievements of workers and to celebrate the labor movement.
Over time, the meaning of Labor Day has changed somewhat. It’s still a day to celebrate workers and their achievements, but it has also become a day for barbecues, picnics, and other outdoor activities. For many Americans, it marks the end of summer and the start of the school year. No matter how you choose to spend your Labor Day, one thing is for sure: it’s a day to kick back and enjoy some well-deserved time off!
There you have it: a brief history of Labor Day. Next time you’re enjoying a cookout or taking a leisurely stroll on this day off from work, remember that it exists because workers fought—and sometimes died—for the right to a fair wage and reasonable working hours. We hope you have a safe and enjoyable Labor Day!
In the United States, Labor Day is celebrated on the first Monday of September. It’s a day off for many workers, and a time to enjoy the last few days of summer, but did you know that Labor Day is more than just a day off from work? This American institution has a long and interesting history so let’s take a quick look at the origins of Labor Day and how it’s evolved over the years.
Labor Day has its roots in the labor movement of the late 19th century. At that time, working conditions were often very dangerous, and workers were frequently required to work long hours for little pay. In an effort to improve these conditions, workers began organizing into unions. On September 5, 1882, 10,000 workers took unpaid leave and marched in New York City to demand better working conditions. The following year, another labor parade was held in New York City. Inspired by these events, workers across the country began holding their own parades and rallies on the first Monday in September.
In 1884, the first formal proposal to make Labor Day a national holiday was made at a meeting of the Central Labor Union. The proposal was approved, and the first National Labor Day was celebrated on September 5, 1884. In 1894, Congress passed a law making the first Monday in September, a national holiday, Labor Day. The first Monday in September was selected as the official date for a few reasons: first, it allowed workers a three-day weekend (as Friday and Saturday were already days off); second, it prevented summer vacations from being cut short; and third, it avoided competition with Independence Day celebrations. Today, Labor Day is celebrated in countries around the world to recognize the achievements of workers and to celebrate the labor movement.
Over time, the meaning of Labor Day has changed somewhat. It’s still a day to celebrate workers and their achievements, but it has also become a day for barbecues, picnics, and other outdoor activities. For many Americans, it marks the end of summer and the start of the school year. No matter how you choose to spend your Labor Day, one thing is for sure: it’s a day to kick back and enjoy some well-deserved time off!
There you have it: a brief history of Labor Day. Next time you’re enjoying a cookout or taking a leisurely stroll on this day off from work, remember that it exists because workers fought—and sometimes died—for the right to a fair wage and reasonable working hours. We hope you have a safe and enjoyable Labor Day!
Fun Fact: As of 2021, 65% of Americans believe there is intelligent life on other planets!
Stephanie’s Section
Aliens vs. Voyager 1 Do you believe in aliens? It’s a question that has been debated for centuries, and there is still no clear answer. There are those who firmly believe that aliens exist, and others are convinced that aliens are nothing more than a figment of our imagination. There is no right or wrong answer, but it’s certainly an interesting topic to debate. Recently, Voyager 1 has been at the center of this very debate. How and why? You may be wondering what is Voyager 1? Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, to study the outer solar system and interstellar space beyond the sun’s heliosphere. Voyager 1 has been in operation for almost 45 years, and still transmits data back to earth through the Deep Space Network! Recently, Nasa’s engineering team is investigating a mystery taking place on the Voyager 1 spacecraft. The vehicle is more than 11 billion miles from Earth, and for the past several months has been sending back strange readings that have left engineers baffled. As the most distant human-made object from Earth, Voyager 1 is operating at the edge of the solar system, beyond the Sun’s influence, and while the craft is successfully receiving and executing commands from Earth, the readouts from the probe’s AACS (attitude articulation and control system) show something strange is happening on board. The AACS maintains the craft’s orientation, keeping the antenna pointed directly at Earth so that data can be successfully sent back to Nasa. While all indicators suggest the AACS is working as normal, the readings show that something is interfering with the spacecraft’s ability to communicate with Earth. The interference is coming from an unknown source and it’s preventing Voyager 1 from sending back data at its full capacity. It appears Voyager 1 is detecting a never-before-seen interaction between particles from inside our solar system and particles from interstellar space. This is something that was not predicted by models of how these particles should behave. The new findings have been published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, and they could help scientists to better understand the environment around Voyager 1, as well as the transition between our solar system and interstellar space. “The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated. We’re also in interstellar space – a high-radiation environment that no spacecraft have flown in before. So there are some big challenges for the engineering team. But I think if there’s a way to solve this issue with the AACS, our team will find it” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and 2 at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Source Although the interference is preventing Voyager 1 from functioning at its full capacity, and the team is working to determine the cause of the interference, they haven’t been able to find a definitive answer. They’re confident that they’ll eventually be able to solve the mystery and figure out what’s causing the strange signals. This isn’t the first time that Voyager 1 has picked up strange signals. In 1977, the spacecraft recorded a series of pulses that were later determined to be from two objects colliding in deep space. The last time we picked up strange signals onboard the Voyager 1 it was later explained, but many have theorized that the spacecraft is now picking up signals from an unknown intelligent life form and that’s what is causing the interference. So, what do you believe? Are aliens causing the interference onboard Voyager 1? Search by Zip to Find Applicable Energy Laws
Search by Zip to Find Applicable Energy Laws
There are over 30 cities/states with Energy Benchmark requirements - 16 have Energy Audit requirements as well! Use this free tool to check if your building has an upcoming Energy Benchmark or Energy Audit deadline.
FIND OUT HERE »
